Definition of Sustainability in Architecture
Sustainability in architecture refers to the practice of designing and constructing buildings that aim to minimize their environmental impact while maximizing resource efficiency. This involves considering factors such as energy consumption, water usage, waste management, and the overall life cycle of a building. Sustainable architecture also takes into account the well-being of occupants, focusing on creating healthy and comfortable indoor environments.
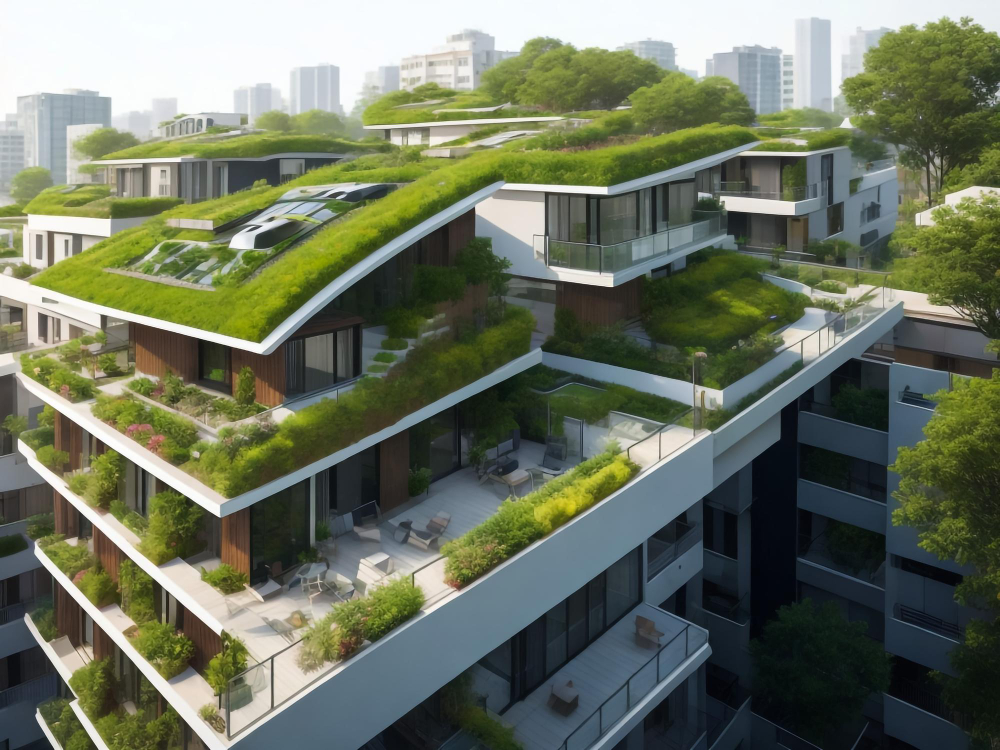

In essence, sustainability in architecture strives to create buildings that are harmonious with their surroundings, contribute positively to the community, and maintain a balance between economic, social, and environmental considerations. It is about designing spaces that not only meet the needs of present generations but also ensure that future generations can continue to thrive in a healthy and thriving environment.
• Sustainable architecture aims to minimize environmental impact and maximize resource efficiency
• Factors considered include energy consumption, water usage, waste management, and building life cycle
• Focus on creating healthy and comfortable indoor environments for occupants
• Buildings should be harmonious with surroundings and contribute positively to the community
• Balance between economic, social, and environmental considerations is crucial in sustainable architecture.
Importance of Green Building Design in Today’s Society
Green building design plays a pivotal role in addressing pressing environmental issues such as climate change, resource depletion, and pollution. By incorporating sustainable practices into architectural projects, buildings can significantly reduce their carbon footprint, energy consumption, and overall environmental impact. This is crucial in today’s society where the need for sustainable development and eco-friendly solutions is more urgent than ever.
Furthermore, green buildings promote healthier indoor environments for occupants by using natural light, improving air quality, and utilizing non-toxic materials. This has a direct positive impact on human health and well-being, leading to increased productivity, reduced absenteeism, and overall enhanced quality of life. In a world where urbanization is rapidly increasing and the construction industry is a major contributor to environmental degradation, the importance of green building design in today’s society cannot be overstated.
Integration of Sustainable Practices in Architectural Education
Incorporating sustainable practices within architectural education is crucial in preparing future designers to address environmental challenges. By integrating concepts like energy efficiency, passive design strategies, and green building materials into the curriculum, students can develop a deep understanding of how their design choices impact the environment. Hands-on experiences, such as sustainable design projects and research initiatives, can further enhance students’ practical skills and knowledge in creating environmentally-conscious architectural solutions.
Engaging students in critical discussions about the social, economic, and environmental implications of their design decisions fosters a holistic approach to sustainable design. By encouraging collaboration among students from different disciplines, such as engineering, environmental science, and architecture, educational institutions can create a dynamic learning environment that reflects the interdisciplinary nature of sustainable design. Moreover, inviting industry professionals to share their expertise and experiences can provide students with valuable insights into real-world sustainability practices and challenges.
Challenges Faced in Implementing Green Building Design in Education
Implementing green building design in education comes with its fair share of challenges. One major obstacle is the lack of resources and funding allocated to support sustainable practices in architectural programs. Many educational institutions struggle to invest in modern technologies, materials, and training necessary for students to gain hands-on experience in sustainable design. Without proper financial backing, it becomes difficult to stay updated with the latest advancements in green building practices and incorporate them effectively into the curriculum. Moreover, limited faculty expertise in sustainable design can hinder the development of comprehensive educational programs focused on environmental consciousness.
Another significant challenge in integrating green building design into educational settings is the resistance to change from traditional teaching methods. Overcoming entrenched ideologies and practices that prioritize conventional architectural approaches over sustainable design principles can be a daunting task. Educators and administrators often face pushback from stakeholders who may not fully understand the benefits or importance of incorporating sustainability into architectural education. This resistance to change can impede progress towards creating a curriculum that adequately prepares students to address the environmental challenges of modern society through innovative and sustainable design solutions.
Case Studies of Successful Sustainable Architectural Projects
Some exemplary sustainable architectural projects have set notable benchmarks in the industry. The Bullitt Center in Seattle, designed to be the greenest commercial building in the world, reflects a commitment to energy efficiency and environmentally friendly practices. Its innovative features such as a solar panel-clad roof, rainwater harvesting system, and composting toilets have significantly reduced its environmental impact while providing a healthy and productive workspace for occupants. This project demonstrates how sustainable architectural design can create spaces that prioritize both environmental conservation and human well-being.
Similarly, The Edge in Amsterdam showcases cutting-edge sustainable design principles. This futuristic office building not only harnesses renewable energy sources such as solar power but also integrates smart technologies for optimal energy management. With a strong emphasis on natural lighting, green spaces, and resource-efficient systems, The Edge exemplifies how sustainability can be seamlessly woven into architectural design to create spaces that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also environmentally responsible.
Innovative Technology and Materials Used in Green Building Design
In the realm of green building design, innovative technology and materials play a vital role in shaping the future of sustainable architecture. Architects and designers are constantly exploring cutting-edge technologies and eco-friendly materials to create buildings that are energy-efficient, environmentally friendly, and visually appealing.
From solar panels and green roofs to advanced insulation and recycled materials, the field of green building design is continuously evolving to incorporate the latest innovations. These technologies and materials not only help reduce the environmental impact of buildings but also contribute to creating healthier and more comfortable spaces for occupants.
Collaboration Between Architects, Educators, and Industry Professionals for Sustainable Design
Architects, educators, and industry professionals play a critical role in advancing sustainable design practices within the architecture field. By collaborating closely, these stakeholders can leverage their unique expertise and perspectives to develop innovative solutions that prioritize environmental responsibility and social well-being. Architects bring design creativity and technical knowledge to the table, educators offer valuable insights into pedagogy and research, while industry professionals bring practical experience and cutting-edge technology to the forefront of sustainable design initiatives.
This collaborative effort fosters a holistic approach to sustainable architecture, where interdisciplinary teamwork allows for the integration of diverse viewpoints and skill sets. Through ongoing communication and knowledge-sharing, architects, educators, and industry professionals can co-create sustainable solutions that not only meet the needs of today’s society but also anticipate and address the challenges of tomorrow. By working together towards a common goal of promoting sustainable design principles, these stakeholders can drive positive change and shape the future of architectural practice for the better.
The Role of Government Policies in Promoting Sustainable Architecture Education
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping the direction of sustainable architecture education. By implementing regulations and incentives that encourage the incorporation of sustainable practices in architectural curriculum, governments can significantly impact the future of the industry. These policies serve as a framework for educators, institutions, and students to prioritize sustainability and environmental consciousness in their design processes and decision-making.
Furthermore, government support can create a ripple effect throughout the architectural community, fostering a culture of innovation and collaboration towards sustainable design solutions. By providing funding opportunities, grants, and resources specifically targeted towards sustainable architecture education, governments can empower future professionals to lead the way in creating environmentally responsible and resilient built environments.
Benefits of Incorporating Sustainability in Architectural Curriculum
Incorporating sustainability in architectural curriculum offers numerous benefits to students and the industry alike. By integrating principles of sustainable design into their education, future architects gain a deep understanding of environmental impact, energy efficiency, and resource conservation. This knowledge equips them to create buildings that not only meet current needs but also consider the long-term effects on the environment and society. Furthermore, a curriculum that emphasizes sustainability encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills among students, preparing them to address complex challenges in the field of architecture.
Another key advantage of incorporating sustainability in architectural education is the promotion of innovation and creativity. By challenging students to think outside the box and explore alternative solutions, sustainable design principles spark new ideas and approaches to building practices. This creative process fosters a culture of continuous improvement and experimentation, leading to the development of innovative architectural solutions that minimize environmental impact and enhance the quality of life for occupants.
The Future of Green Building Design in Architectural Education
As we look ahead to the future of green building design in architectural education, it is clear that integrating sustainable practices into the curriculum will be paramount. With an increasing focus on environmental concerns and the urgent need for sustainable solutions, it is essential for architectural students to learn how to design buildings that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also environmentally responsible. By incorporating courses on green building techniques, materials, and technologies, educational institutions can prepare future architects to meet the growing demand for sustainable design.
Moreover, the future of green building design in architectural education will also involve fostering collaboration between students, educators, and industry professionals. By creating opportunities for hands-on experience through internships, workshops, and collaborative projects, students can gain valuable insights into the practical application of sustainable design principles. This interdisciplinary approach will not only enrich the learning experience but also equip students with the skills and knowledge needed to address complex sustainability challenges in their future architectural practice.
Measuring the Success of Sustainable Architectural Education Programs
For sustainable architectural education programs, measuring success involves assessing the extent to which students have internalized sustainability principles and practices. This can be evaluated through the incorporation of sustainability metrics in student projects and the analysis of their understanding of sustainable design concepts. Additionally, tracking post-graduation achievements and the impact students have on real-world projects can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of these educational programs.
Another way to measure the success of sustainable architectural education programs is to analyze the integration of sustainability into the curriculum and coursework. By examining the range and depth of sustainability topics covered, the presence of hands-on experiences such as sustainable design projects or internships, and the level of engagement with industry professionals, educators can gauge the overall effectiveness of these programs in preparing students for careers in sustainable architecture. Additionally, feedback from alumni and employers on the practical application of sustainability knowledge gained during their education can offer valuable perspectives on the program’s success.
Recommendations for Improving Sustainability in Architectural Education
To enhance sustainability in architectural education, it is imperative to prioritize hands-on learning experiences that allow students to engage directly with sustainable design principles. Incorporating real-world projects and case studies into the curriculum can provide students with practical insights and skills that they can apply in their future careers. Additionally, fostering a collaborative environment where students work closely with industry professionals and educators can offer a holistic perspective on sustainable design practices.
Furthermore, integrating cutting-edge technology and tools, such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) software and energy simulation programs, into the curriculum can equip students with the necessary technical skills to design and evaluate sustainable buildings. By staying abreast of advancements in green building technology, architectural education can better prepare students to meet the evolving demands of the industry and drive innovation in sustainable design practices.
Additional Resources:
[catlist categorypage=”yes”]
[newsletter]
Table of Contents
Categories:
[categories orderby=name]
Latest Posts:
[sbs_latest_posts]
FAQs:
What is the definition of sustainability in architecture?
Sustainability in architecture refers to designing and constructing buildings that have minimal negative impact on the environment, are energy-efficient, and promote the well-being of occupants.
Why is green building design important in today’s society?
Green building design is important in today’s society as it helps reduce energy consumption, lower carbon emissions, conserve natural resources, and create healthier indoor environments.
How can sustainable practices be integrated into architectural education?
Sustainable practices can be integrated into architectural education through incorporating courses on green building design, promoting research on sustainable technologies, and encouraging hands-on projects that focus on sustainability.
What are some challenges faced in implementing green building design in education?
Some challenges in implementing green building design in education include limited resources, resistance to change, and the need for specialized training for educators.
What are some benefits of incorporating sustainability in architectural curriculum?
Benefits of incorporating sustainability in architectural curriculum include preparing students for the changing industry, promoting innovative thinking, and creating a more environmentally conscious generation of architects.
How can the success of sustainable architectural education programs be measured?
The success of sustainable architectural education programs can be measured through student outcomes, industry partnerships, research publications, and the impact of sustainable design projects on the community.

 and then
and then